While driving your car, have you ever caught a whiff of something that reminded you of cleaning supplies? If so, you may have experienced the infamous “ammonia smell” of car exhausts. And, one question that frequently comes up is why car exhaust smells like ammonia.
Well, here’s a short explanation. When nitrogen elements (NOx) from the exhausts react with hydrogen from the fuels in the car’s catalytic converter, ammonia generates. This is the source of the ammonia smell in car exhaust. Or, the ammonia smell could also arise due to a leakage in the diesel exhaust fluid (DEF).
Now, to prevent this phenomenon, you have to learn more about how this process works and what you can about it. So, keep reading to find out!!
Why Car Exhaust Smells Like Ammonia (In-depth Explanation)
Car exhaust smells like ammonia due to a chemical reaction that occurs within the catalytic converter. Now, when the engine is running, it burns fuel and produces exhaust gases from various chemicals. One of the chemicals present in exhaust gasses is nitrogen oxide (NOx).
The catalytic converter is designed to reduce the amount of NOx in exhaust gases by converting it into nitrogen (N2) and water (H2O).
However, this process is not always perfect, and sometimes the NOx is not fully converted. If this happens, the remaining NOx can react with the hydrogen(H2) present in the exhaust gasses to form ammonia (NH3), according to a 2021 scientific research.

Ammonia has a strong and pungent smell, and it is a smell that is often associated with car exhaust. The presence of ammonia in the exhaust gases is an indication that the catalytic converter is not functioning correctly.
Car Exhaust Smells Like Ammonia: What’s the solution for it?
Well, the general solution for this problem is to replace the problematic catalytic converter with a new one.
Remember, though the catalytic converter is the main culprit for this issue, this can also be caused by a variety of factors, including a malfunctioning engine, a clogged catalytic converter, or a damaged exhaust system.

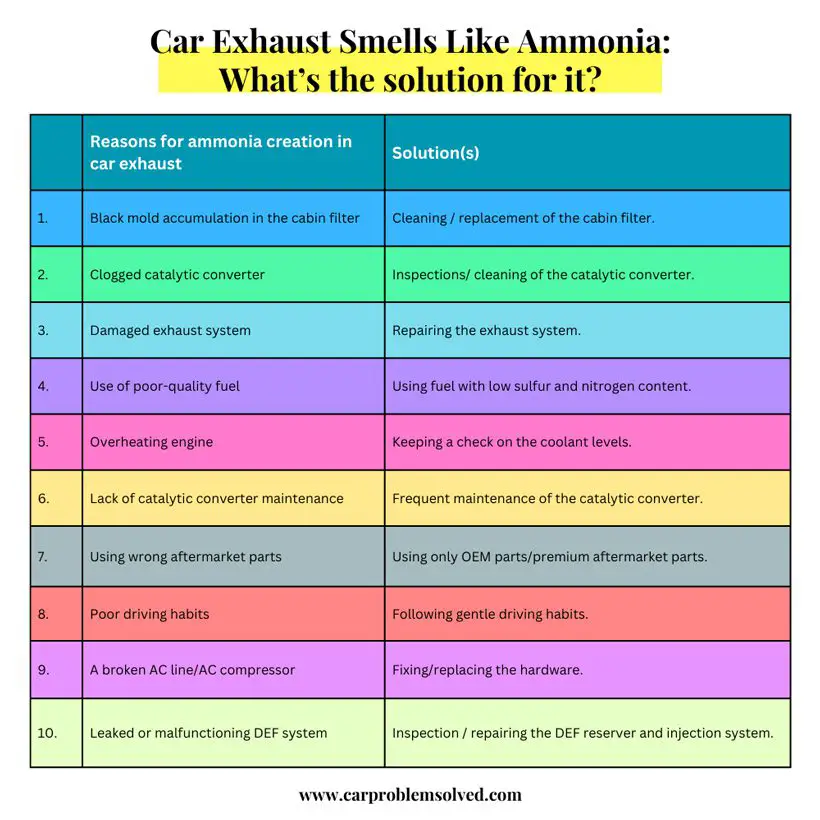
Likewise, the solution to this problem is varied, as well. So, I’ve arranged them in a nice table for you below:
| Reasons for ammonia creation in car exhaust | Solution(s) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Black mold accumulation in the cabin filter | Cleaning / replacement of the cabin filter. |
| 2. | Clogged catalytic converter | Inspections/ cleaning of the catalytic converter. |
| 3. | Damaged exhaust system | Repairing the exhaust system. |
| 4. | Use of poor-quality fuel | Using fuel with low sulfur and nitrogen content. |
| 5. | Overheating engine | Keeping a check on the coolant levels. |
| 6. | Lack of catalytic converter maintenance | Frequent maintenance of the catalytic converter. |
| 7. | Using wrong aftermarket parts | Using only OEM parts/premium aftermarket parts. |
| 8. | Poor driving habits | Following gentle driving habits. |
| 9. | A broken AC line/AC compressor | Fixing/replacing the hardware. |
| 10. | Leaked or malfunctioning DEF system | Inspection / repairing the DEF reserver and injection system. |
Now, let’s dive a bit deeper into these facts:
1. Black mold accumulation in the cabin filter:
The accumulation of black mold in the cabin filter can produce a strong smell of ammonia that resembles the smell of urine.
Solution:
Regular cleaning or replacement of the cabin filter is necessary to prevent this. Plus, keeping the interior of the vehicle dry to prevent mold growth is also essential here.
2. Clogged catalytic converter:
A clogged catalytic converter cannot convert nitrogen oxides (into less harmful compounds). So, it leads to a higher concentration of nitrogen oxides in the exhaust gasses.
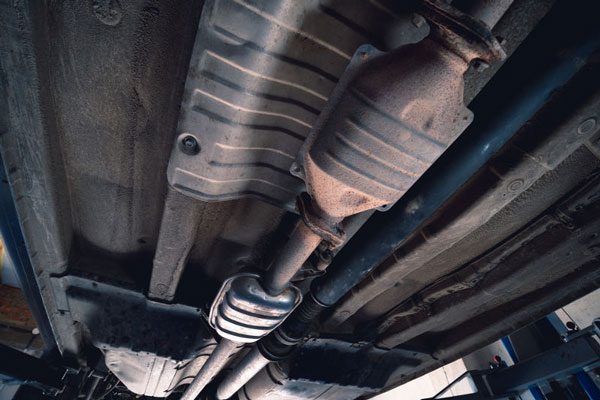

Solution:
Regular inspections and cleaning of is recommended here to ensure proper function of the catalytic converter.
3. Damaged exhaust system:
A damaged exhaust system can allow more nitrogen oxides to escape into the atmosphere, increasing the concentration of nitrogen oxides in the exhaust gases.

Solution:
Repairs of the exhaust system are necessary in this case to ensure proper function.
4. Use of poor-quality fuel:
Poor-quality fuel contains more sulfur and other impurities that can damage the catalytic converter and increase the formation of ammonia.
Solution:
Use of high-quality fuel with low sulfur and nitrogen content is the optimal solution for this problem.
5. Overheating engine
Overheating the engine can also cause the catalytic converter to overheat and break down, leading to the formation of ammonia.

Solution:
To prevent this issue, make sure that the engine doesn’t overheat by keeping a check on the coolant level and the cooling system.
6. Lack of catalytic converter maintenance
Lack of maintenance can cause the catalytic converter to malfunction and break down, leading to the formation of ammonia.
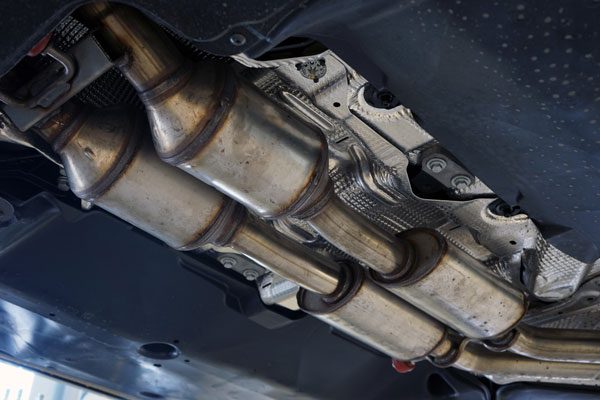

Solution:
It is officially recommended by many automotive manufacturers (such as Group1Automotive) that maintenance be conducted on the catalytic converter after every 50,000 miles. Therefore we also recommend doing such rigorous maintenance to your catalytic converters.
7. Using aftermarket parts
Using aftermarket parts that are not designed for the vehicle can damage the catalytic converter. This can lead to the formation of ammonia.
Solution:
So, using only OEM parts or high-quality aftermarket parts that are designed for the specific vehicle is the legit solution to prevent this issue.
8. Poor driving habits
Poor driving habits such as excessive idling, hard braking, and acceleration can burn excess fuel (as reported by the Canada Govt.). This can lead to the formation of ammonia.
Solution:
In cases like this, following gentle driving habits and maintaining a consistent driving speed is the indispensable solution.
9. Broken AC line/AC compressor
Sometimes the AC line is broken and the coolant responsible for air conditioning in your car gets leaked. This leakage can also occur due to a faulty compressor as well.

Solution:
If your AC is blowing hot air and, at the same time, your car is smelling like ammonia, you can be sure that the broken AC line is responsible for the smell. In this case, you must have your air conditioning hardwares fixed by a professional auto mechanic to solve this.
10. Leaked or malfunctioning DEF system
The DEF (diesel exhaust fluid) in a car is a direct ammonia-based liquid. The DEF system injects and mixes the DEF liquid to the NOx (harmful) gases and transforms them into plain N2 (harmless) gas. The system is supposed to only inject the DEF liquid when the car is running and emitting NOx gases (not when the car is idle).
Now, if there is any leakage in the DEF system in your car, or if it is injecting the liquid even when your car is idle, you will surely smell ammonia.
Solution:
The only solution for this is to have a professional auto mechanic check your DEF system. This will make sure that your DEF system does not have any leak, or is not malfunctioning.
Which Car Models Are More Prone To The Issue Of Ammonia Creation In Exhaust?
Older car models (manufactured before 2005) are more prone to the issue of ammonia creation in the exhaust.
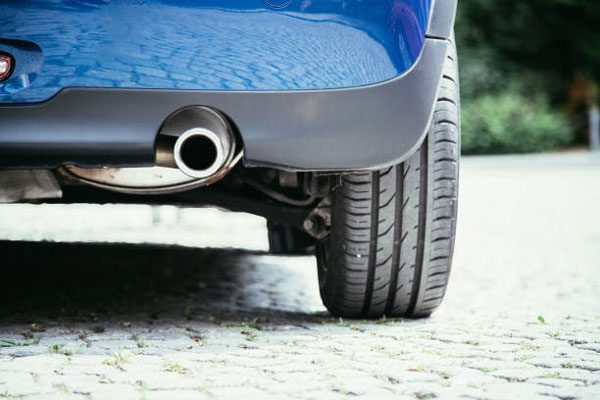

Here are a few reasons why:
1. Lack of emission control technology:
Older car models were not equipped with the same emission control technology that modern cars have. This means that older cars emit more nitrogen oxides, which can then react with hydrogen to form ammonia.
2. Age-related wear and tear:
As cars age, they are more likely to experience wear and tear on various components, such as the engine, exhaust system, and catalytic converter. This can lead to increased emissions and the formation of ammonia.
3. Lack of regular maintenance:
Older car models may not have been maintained as regularly as modern cars, which can lead to the formation of ammonia.

4. Use of leaded fuel
Older cars were designed to use leaded fuel, which can damage the catalytic converter quicker and increase the formation of ammonia.
5. Use of poor-quality fuel:
Older cars are more prone to using poor-quality fuel which can damage the catalytic converter and increase the formation of ammonia.
To avoid these issues, we recommend frequently maintaining and inspecting your car (especially if it’s an old one) for potential problems. We also endorse the use of low-nitrogen fuels to minimize the formation of ammonia.
If you’re dealing with an ammonia-like smell from your car exhaust, you may also be interested in our articles on why your car smells like burning rubber or why your car smells like burning oil when idling. Our article on why your car smells like burning rubber discusses the common causes of this smell, such as a slipping drive belt, a damaged serpentine belt, or a malfunctioning accessory pulley. Meanwhile, our article on why your car smells like burning oil when idling explains the possible causes of this smell, such as a leaking valve cover gasket, a worn-out PCV valve, or a damaged engine block. If you’re experiencing any of these smells in your car, our articles can help you diagnose and fix the problemFAQs
Now, let’s know the answers to some commonly asked queries regarding this topic:
Yes, it is indeed a matter of concern. Ammonia is a toxic chemical that can cause irritation to the eyes, nose, and throat, as well as headaches and other symptoms. Long-term exposure to ammonia can also lead to more serious health problems such as lung damage and cancer.
Yes, it is harmful for your health to smell ammonia in your car. It is because the fumes produced by the ammonia can irritate the eyes, nose, and throat.
And it can also lead to headaches and other symptoms. Long-term exposure to the chemical can also lead to more serious health problems, such as lung damage and cancer.
Sometimes people mistake hydrogen sulfide (H2S) for ammonia (NH3) in their car exhaust, as both chemicals have an irritating smell that can be difficult to distinguish.
However, ammonia has a sharp smell that is often described as similar to human urine products. Hydrogen sulfide, on the other hand, has a rotten egg smell.
Conclusion
Now that you’ve got a clear understanding on why car exhaust smells like ammonia. Car exhaust smells like ammonia due to the chemical reaction of nitrogen oxides and hydrogen in the catalytic converter.
The presence of ammonia in the exhaust gasses is an indication that the converter is not functioning correctly. So, regular maintenance of the engine and exhaust system can prevent this from happening.
If you notice a strong ammonia smell in your car’s exhaust, it’s time to have it inspected by a professional.
